![]()
These key principles guide the creation of a curriculum that not only imparts knowledge but also nurtures the holistic development of students, preparing them to thrive in both personal and societal contexts.
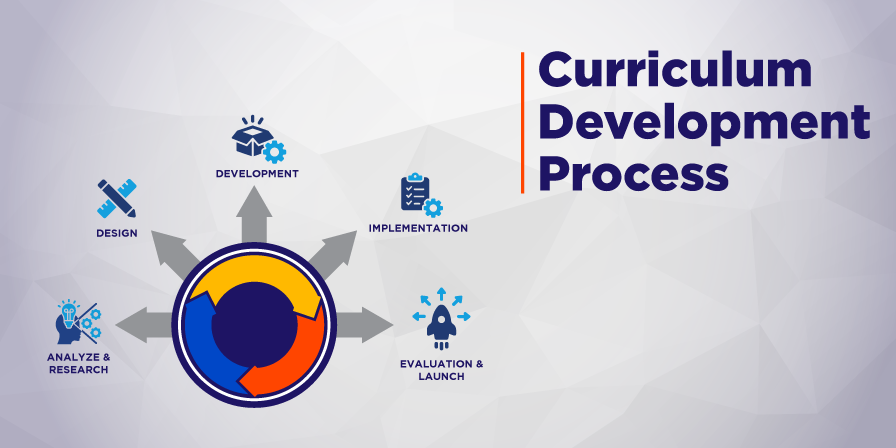
1. Totality of Experiences
This principle emphasises that the curriculum should encompass all learning experiences, both inside and outside the classroom, to ensure holistic development. In real-world curriculum development, this means integrating academic content with extracurricular activities, life skills, and community engagement to create well-rounded individuals.
2. Child-Centredness
A child-centred curriculum focuses on students’ needs, interests, and developmental stages. This principle is applied by tailoring educational content and teaching methods to suit individual students’ learning styles and paces, ensuring that education is relevant and engaging.
3. Conservation and Creativity
Balancing the preservation of cultural and traditional values with the encouragement of innovation and creativity is key to curriculum development. In practice, this principle is reflected in curricula incorporating foundational knowledge and opportunities for creative expression and critical thinking.
4. Integration
Integration involves connecting different subjects and learning experiences to create a cohesive and interconnected curriculum. Real-world application of this principle includes interdisciplinary projects and thematic units that help students see the relationships between different areas of knowledge.
5. Flexibility
Flexibility in curriculum development allows for adjustments based on students’ needs, societal changes, and advancements in knowledge. This principle is applied by designing curricula that can be adapted to different contexts, learning environments, and individual student requirements.
6. Mental Discipline
This principle focuses on developing students’ intellectual rigour and discipline through challenging content and activities. It is applied by including problem-solving exercises, critical thinking tasks, and analytical discussions that push students to think deeply and systematically.
7. Character Formation
Curriculum development shapes students’ moral and ethical values, fostering character development. This principle is implemented by integrating lessons on empathy, responsibility, and citizenship into the curriculum, helping students grow as principled individuals.
8. Social Fulfilment
Curriculum prepares students to fulfill their societal roles effectively, contributing to the common good. This is achieved by incorporating social studies, community service projects, and societal discussion, ensuring students understand and engage with the world around them.
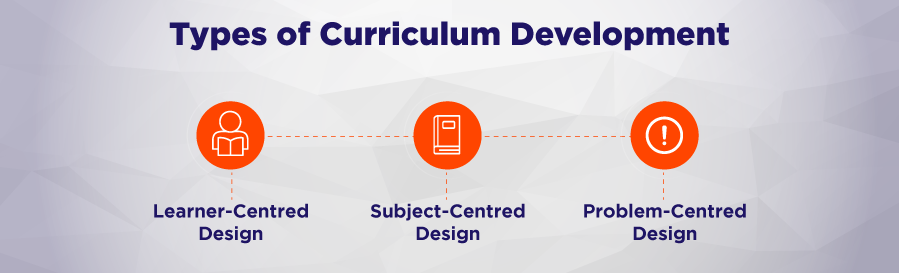
Traditional vs Modern Approaches to Curriculum Development
Traditional Curriculum Planning Approaches
Traditional curriculum planning is often characterised by a rigid, subject-centred approach emphasising standardised content delivery and rote learning. This method focuses on the mastery of established knowledge and often follows a fixed structure, where educational authorities determine the curriculum and leave little room for flexibility.
The benefits of this approach include consistency in educational standards and clear benchmarks for student achievement. However, the challenges lie in its limited adaptability to individual student needs and its tendency to overlook creativity and critical thinking.
Modern Curriculum Development Practices
In contrast, modern approaches to curriculum planning are more dynamic and learner-centred. These approaches prioritise flexibility, integration, and the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Modern curricula often incorporate interdisciplinary learning, technology, and real-world applications, making education more relevant and engaging for students.
The benefits of this approach include enhanced student motivation, personalised learning experiences, and the ability to adapt to rapidly changing societal needs. However, the challenges include the complexity of implementation, the need for continuous teacher training, and the potential for inconsistent educational outcomes.